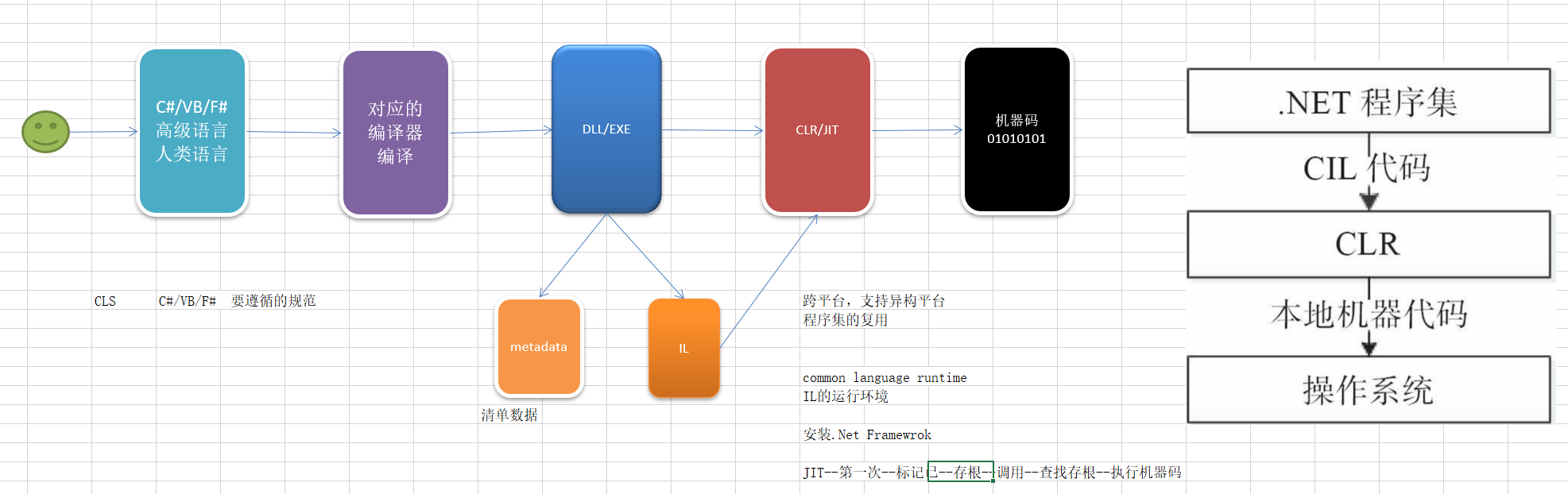
1.CLR
就是一个IL与机器码(win linux)之间的一个适配器,通过JIT的编码让机器码能编译执行
2.堆栈
堆Heap:一个程序运行时,该进程存放引用类型变量的一块儿内存,全局唯一!
栈Stack:先进后出数据结构,线程栈,一个线程存放变量的内存,随着线程生命周期
3.值类型/引用类型
值类型长度能确定的,引用类型长度不能确定的
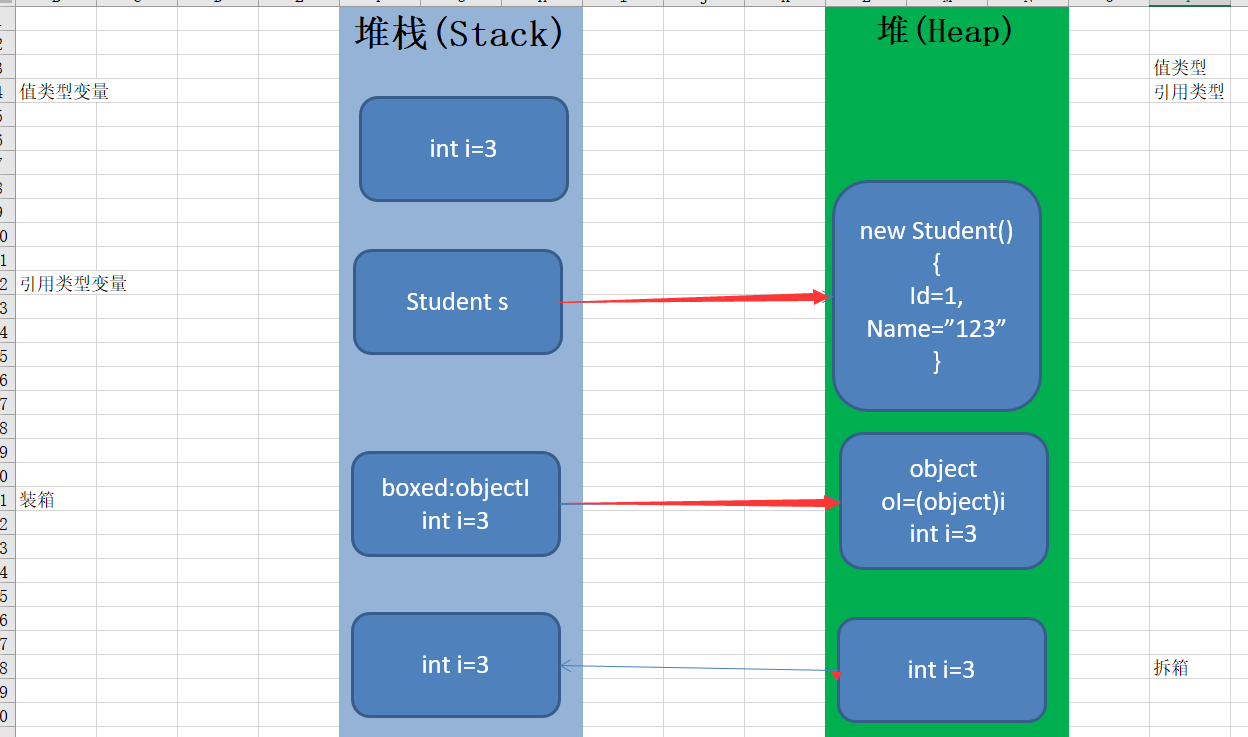
值类型分配在栈上,如:结构 枚举,
引用类型分配在堆上, 如:类 接口 委托
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| {
ReferencePoint referencePoint = new ReferencePoint(123);
Console.WriteLine(referencePoint.x);
}
{
int i = 3;
object oValue = i;
int k = (int)oValue;
}
|
引用/值类型的位置在哪里?
总结:值类型的值,会随着对象的位置存储,引用类型的值,一定在堆里面。
值类型的长度是确定的。引用类型的长度是不确定的,只有堆才能放各种值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
{
ReferencePoint referencePoint = new ReferencePoint(3);
Console.WriteLine(referencePoint.x);
ValuePoint valuePoint = new ValuePoint();
valuePoint.Text = "123";
}
public class ReferencePoint
{
public int x;
public ReferencePoint(int x)
{
this.x = x;
}
}
public struct ValuePoint
{
public int x;
public ValuePoint(int x)
{
this.x = x;
this.Text = "1234";
}
public string Text;
}
|
引用类型在推中的分配,是开辟连续空间,引用类型的大小是怎么分配的?
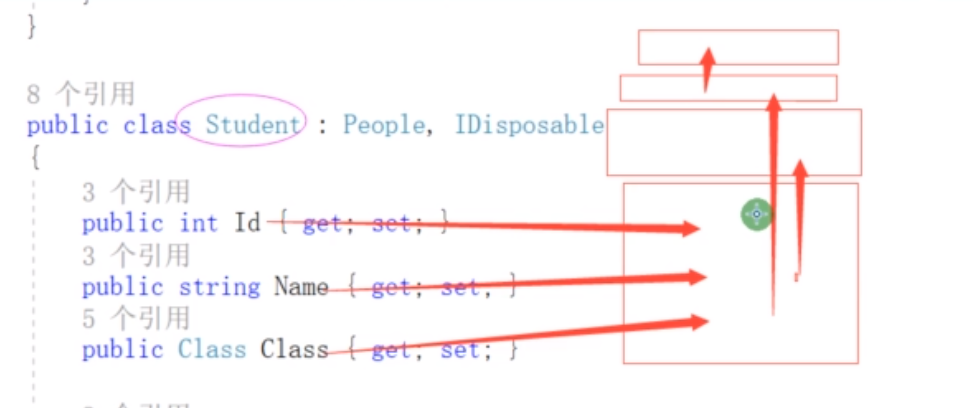
如:
Id ->指向一块分配的内存地址
Name->指向一块分配的内存地址
Class->指向一块分配的对象的内存地址
创建一个引用类型,在推中相当于会分配N个内存地址块。
String类型的享元模式
在堆中已经分配的资源,如果重新创建时,发现堆里面已存在,则不会新分配内存,新创建的对象地址会直接指向已存在的内存地址。
如果新分配内存的则不会
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
string student = "大山";
string student2 = "APP";
student2 = "大山";
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(student, student2));
student2 = "大山1";
Console.WriteLine(student);
string student3 = string.Format("大{0}", "山");
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(student, student3));
string student4 = "大" + "山";
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(student, student4));
string halfStudent = "山";
string student5= "大" + halfStudent;
Console.WriteLine(object.ReferenceEquals(student, student5));
|
4.内存回收
回收是由CLR提供的GC来操作的
1 什么样的对象需要垃圾回收?
托管资源+引用类型
2 什么是托管资源和非托管资源?
托管的就是CLR控制的,new的对象 ,string字符串 ,变量
非托管不是CLR能控制的,数据库连接、文件流、句柄、打印机连接;
using(SqlConnection)被C#封装了管理了那个非托管的数据库连接资源,
只要是手动释放的,都是非托管的
3 哪些对象的内存,能被GC回收?
对象访问不到了,那就可以被回收了
程序–入口–去找对象–建立对象图–访问不到的就是垃圾,如static的对象就不会被回收
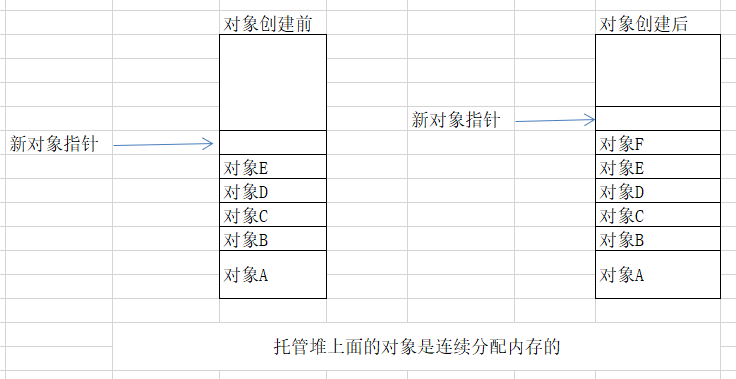
4 对象是如何分配在堆上?
连续分配在堆上面,每次分配就先检查空间够不够
5 什么时候执行GC
a) new对象时–临界点
b) GC.Collect 强制GC
c) 程序退出时会GC
GC.Collect 可以GC,但是频繁GC是不好的,GC是全局的
项目中有6个小时才运行new一次,什么时候GC? 不GC,可以手动GC
6 GC的过程是怎么样的呢?
N个对象–全部对象标记为垃圾–入口开始遍历–访问到的就标记可以访问(+1)
–遍历完就清理内存–产生不连续内存–压缩–地址移动–修改变量指向—所以会全局阻塞
清理内存分2种情况:
a)无析构函数,直接清理内存
b)把对象转移到一个单独的队列,会有个析构器线程专门做这个(清理慢一些)
通常在析构函数内部是用来做非托管资源释放,因为CLR肯定调用,所以避免使用者忘记的情况
析构函数 GC会在回收时执行此函数:
1
2
3
4
| ~Student()
{
MyLog.Log($"执行{this.GetType().Name}Dispose");
}
|
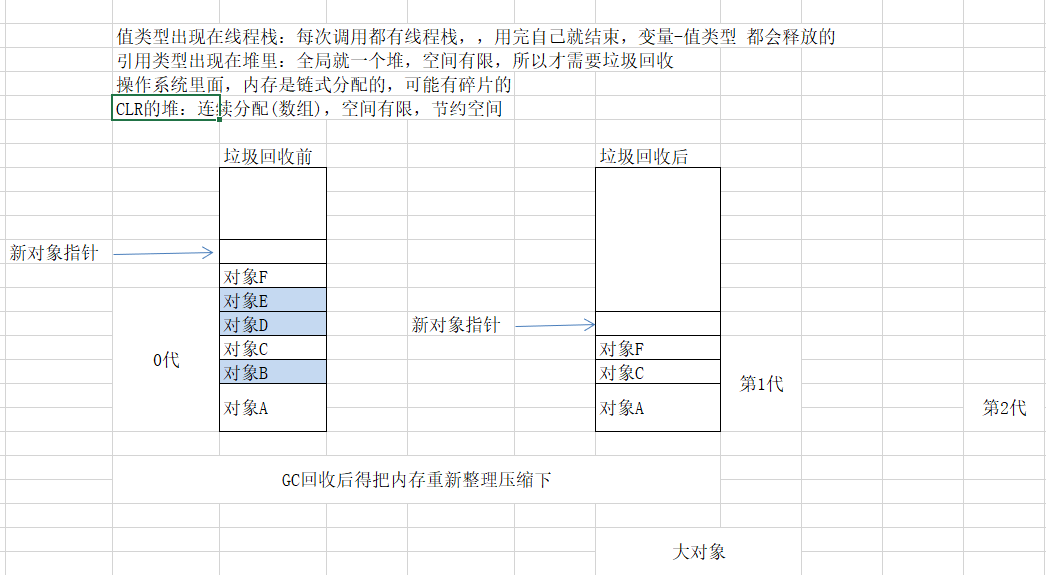
7 垃圾回收策略
对象分代:3代
0代:第一次分配到堆,就是0代
1代:经历了一次GC,已然还在的
2代:经历了两次或以上GC,已然还在的
垃圾回收时,优先回收0代,提升效率,最多也最容易释放
0代不够—找1代—1代不够才找2代–再不够就不够了。。
8 大对象堆
主要作用是为了解决:一是内存移动大对象;二是0代空间问题;
80000字节就叫大对象,没有分代,直接都是2代
5.析构函数Dispose
析构函数:被动清理
Dispose:手动清理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
/// <summary>
/// 标准Dispose模式
///
/// 析构函数:被动清理
/// Dispose:主动清理
/// </summary>
public class StandardDispose : IDisposable
{
//演示创建一个非托管资源
private string _UnmanageResource = "未被托管的资源";
//演示创建一个托管资源
private string _ManageResource = "托管的资源";
private bool _disposed = false;
/// <summary>
/// 实现IDisposable中的Dispose方法
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
this.Dispose(true); //必须为true
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);//通知垃圾回收机制不再调用终结器(析构器),不会再调用析构函数了
}
/// <summary>
/// 必须,以备程序员忘记了显式调用Dispose方法
/// </summary>
~StandardDispose()
{
//必须为false
this.Dispose(false);
}
/// <summary>
/// 不是必要的,提供一个Close方法仅仅是为了更符合其他语言(如C++)的规范
/// </summary>
public void Close()
{
this.Dispose();
}
/// <summary>
/// 非密封类修饰用protected virtual
/// 密封类修饰用private
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing"></param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (this._disposed)//已经被释放的还可以不异常
{
return;
}
if (disposing)
{
// 清理托管资源
if (this._ManageResource != null)
{
//Dispose
this._ManageResource = null;
}
}
// 清理非托管资源
if (this._UnmanageResource != null)
{
//Dispose conn.Dispose()
this._UnmanageResource = null;
}
//让类型知道自己已经被释放
this._disposed = true;
}
public void PublicMethod()
{
if (this._disposed)
{
throw new ObjectDisposedException("StandardDispose", "StandardDispose is disposed");
}
//
}
}
|
PS:内存泄漏 是有对象没有被回收,内存溢出 是指内存不够




